Total Number of SAP Modules
Have you been wondering how many modules does SAP has?
SAP has become crowd-pleasing ERP because of its flexibility and unlimited customization options. If you can invest the time and shower money, then you can drive your car on autopilot mode with SAP. SAP has been divided into various functional modules supporting the processes in executing the business transactions. At a very common level, the modules has been labeled as Financial Accounting (FI), Financial Supply Chain Management (FSCM), Controlling (CO), Materials Management (MM), Sales and Distribution (SD), Logistics Execution (LE), Production Planning (PP), Quality Management (QM), Plant Maintenance (PM), Project System (PS) and Human Resources (HR).
Lets head on over to the eagle eye of a SAP geek. The whole SA P is divided into environments and modules. Due to various functionalities and consequently different needs for flexibilities, SAP continuously aims at introducing loads of new features, upgrades, environments, modules and industry specific solutions to the ERP family.
A) Environments for SAP ERP
1. Supported Hardware: SAP can be installed on the various systems specified below. The functionality and programming stands unchanged.
HP
IBM
Sun
AT&T
AS400
Bull
Sequent
SNI
Compaq Digital
2. Supported Database: SAP is a back-end-free ERP system. It supports the compatibility with various databases without change in the programing or technical aspects
Oracle
MS SQL
Informix
Sybase
Adabas D
DB2 for AIX
DB2/400
3. Supported Operating Systems: SAP can be installed on the following Operating system platforms
MS Windows NT
OS/400
Unix
Solaris
AIX
HP UX
Sinux
B) MODULES in SAP ERP
Basis
ABAP/4 Programming
FI (Financial Accounting)
CO (Controlling)
EC (Enterprise Controlling)
TR (Treasury)
IM (Investment Management)
HR (Human Resource)
SD (Sales and Distribution)
Logistics Information System
MM (Materials Management)
PM (Plant Maintenance)
PP (Production Planning)
QM – Quality Management
BW (Business Warehousing)
IS (Industry Solutions) / SAP for Industries specific solutions
CS (Customer Service)
SMB
CA (Cross Application Components)
PS (Project Systems)
mySAP SEM
mySAP CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
mySAP Product Life Cycle Management
SCM (SAP Supply Chain Management)
Netweaver
mySAP SRM (Supplier Relationship Management)
1. SAP Basis
1.1 Security (BC – SEC)
1.2 Application Link Enabling (ALE)
1.3 Remote Function Calls (RFC)
1.4 Object Linking and Embedding (OLE)
1.5 Common Program Interface Communications (CPI-C)
1.6 Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
1.7 Customizing (BC-CUS)
1.8 ABAP Programming and Runtime Environment (BC – ABA)
1.9 Client Server Technology (BC – CST)
1.10 Network Integration (BC – NET)
1.11 Basis Services/ Communication Interfaces (BC – SRV)
1.12 Computing Center Management System (BC – CCM)
1.13 Upgrade General (BC – UPG)
1.14 Change and Transport System (BC – CTS)
1.15 Operating System Platform (BC – OP)
1.16 Database Interface, database platforms (BC – DB)
1.17 Front End Services (BC – FES)
1.18 ABAP Workbench (BC – DWB)
1.19 Documentation and Translation Tools (BC – DOC)
1.20 Controls and Control Framework (BC – CI)
1.21 Business Management (BC – BMT)
1.22 Middleware (BC – MID)
1.23 Computer Aided Test Tool (BC – CAT)
1.24 Ready to Run R/3 (BC – BRR)
1.25 Authorizations System Monitoring with CCMS Workload Alert Monitor
2. ABAP/4 Programming
2.1 ABAP Workbench
2.2 Menu Painter
2.3 Screen Painter
2.4 Data Dictionary
2.5 SAP Script
2.6 Business Workflow (BC – WF)
2.7 ALE
2.8 EDI
2.9 Business Connector
2.10 Business Server Pages
2.11 Internet Application Server
2.12 Mercator Report Painter
2.13 ALV reporting
2.14 Report writer
2.15 Dialog Programming
2.16 Repository Information System
2.17 ABAP 00
2.18 IDOCS
2.19 LSMW
2.20 Smartforms
2.21 EBP
2.22 ASAP methodology
2.23 ABAP Query
3. SAP FI (Financial Accounting)
3.1 General Ledger Accounting (FI – GL)
3.2 Special Ledger (FI – SL)
3.3 Extended Ledger
3.4 Accounts Payable (FI- AP)
3.5 Accounts Receivable (FI – AR)
3.6 Asset Accounting (FI – AA)
3.7 Bank Accounting
3.8 Funds Management (FI – FM)
3.9 Travel Management (FI-TM)
3.10 Consolidation
4. SAP CO (Controlling)
4.1 Cost Center Accounting (CO – CCA)
4.2 Overhead Cost Controlling (CO – OM)
4.3 Activity Based Coding (CO – ABC)
4.4 Product Cost Controlling (CO – PC)
4.5 Profitability Analysis (CO – PA)
4.6 Material Ledger (CO – ML)
5. SAP EC (Enterprise Controlling)
5.1 Consolidation (EC – CS)
5.2 Executive Information System (EC-EIS)
5.3 Profit Center Accounting (EC – PCA)
5.4 Business Planning and Budgeting
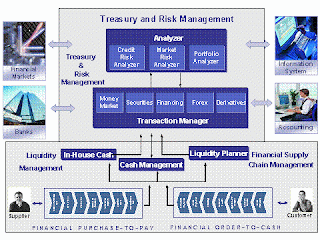
6. SAP TR (Treasury)
6.1 Cash Management (TR – CM)
6.2 Loans Management (TR – LM)
6.3 Market Risk Management (TR – MRM)
6.4 Treasury Management (TR – TM)
6.5 Funds Management (TR – FM)
6.6 Information System
7. SAP IM (Investment Management)
7.1 Investment Programs
7.2 Investment Measures (orders/products)
7.3 Corporation Wide Budgeting
7.4 Appropriation Requests
7.5 Automatic Settlement of Fixed Assets
7.6 Depreciation Forecast
7.7 Information System
8. SAP HR (Human Resource)
8.1 Recruitment
8.2 Personnel Administration
8.3 Benefits Administration
8.4 Compensation Management
8.5 Personnel Development
8.6 Organizational Management
8.7 Travel Management
8.8 Training and Events Management
8.9 Personnel Planning
8.1 Time Management
8.11 Incentive
8.12 Wages
8.13 Workflow
8.14 Payroll
8.15 Internet Scenarios
8.16 Information System
9. SAP SD (Sales and Distribution)
9.1 Master Data
9.2 Sales
9.3 Sales Support
9.4 Sales Information System
9.5 Billing
9.6 Special Business Transactions
9.7 Shipping
9.8 Transportation
9.9 Credit Control
9.10 QM in SD
9.11 Internet
9.12 Foreign Trade
9.13 Electronic Data Interchange
10. SAP Logistics Information System
10.1 Purchasing Information System
10.2 Sales Information System
10.3 Inventory Controlling
10.4 Retail Information System
10.5 Production Planning and Control Information System
10.6 Plant Maintenance Information System
10.7 Project Information System
11. SAP MM (Materials Management)
11.1 Purchasing
11.2 Invoice Verification
11.3 Logistics (General)
11.4 Logistics Information System
11.5 Inventory Management
11.6 Inventory / Valuations
11.7 Materials Planning
11.8 Workflow
11.9 External Services Management
11.10 QM in MM
11.11 Warehouse Management
12. SAP PM (Plant Maintenance)
12.1 Preventative Maintenance
12.2 Maintenance Order Management
12.3 Maintenance Projects
12.4 Service Management
12.5 Maintenance Planning
12.6 Equipment and Technical Objects
12.7 Structuring Technical Systems
12.8 PM Processing
12.9 Work Clearance Management
12.10 Internet Scenarios
12.11 Customizing
12.12 Information System
13. SAP PP (Production Planning)
13.1 Make to Order (CR)
13.2 Make to Order (PIR)
13.3 Repetitive Manufacturing
13.4 PP for Process Industries (PP – PI)
13.5 PP – Processes
13.6 Sales and Operations Planning
13.7 Capacity requirements
13.8 Master Planning
13.9 KANBAN
13.10 Production Orders
13.11 Product Cost Planning
13.12 Plant Data Collection
13.13 Assembly Orders
13.14 Information System
14. SAP QM – Quality Management
14.1 Planning
14.2 Inspections
14.3 Notifications
14.4 Control
14.5 Certificates
14.6 Test Equipment Management
14.7 QM-IS
15. SAP BW (Business Warehousing)
15.1 Data Warehousing
15.2 BI Suite – Business Explorer
15.3 BI Platform
15.4 ODS Structures
15.5 Development Technologies
15.6 Info Cube
15.7 Design Build
16. SAP CS (Customer Service)
16.1 Service Processing
16.2 Controlling
16.3 Service Contracts
16.4 Workflow in Customer Service
17. SAP SMB
18. SAP CA (Cross Application Components)
18.1 SAP Business Workflow
18.2 Application Link Enabling (ALE)
19. SAP PS (Project Systems)
19.1 Basic Data
19.2 Operational Structures
19.3 Project Planning
19.4 Approval
19.5 Information System
19.6 Project Execution and Integration
19.7 Work Breakdown Structure
20. mySAP SRM (Supplier Relationship Management)
20.1 Self Service Procurement
20.2 Service Procurement
20.3 Plan Driven Procurement
20.4 Spend Analysis
20.5 Strategic Sourcing
20.6 Catalogue Content Management
21. mySAP SEM
21.1 Business Consolidation (SEM-BCS)
21.2 Business Information Collection (SEM-BIC)
21.3 Business Planning and Simulation (BW-BPS)
21.4 Corporate Performance Monitor (SEM-CPM)
21.5 Stakeholder Relationship Management (SEM-SRM)
22. mySAP CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
22.1 CRM Enterprise
22.2 Field Applications
22.3 Interaction Center
22.4 E-Commerce
22.5 Channel Management
22.6 Industry Specific CRM
23. mySAP Product Life Cycle Management
23.1 Document Management
23.2 Engineering Change Management
23.3 Enterprise Content Management
23.4 Classification
23.5 Basic Data for Process Manufacturing
24. SAP SCM (SAP Supply Chain Management)
24.1 SCM Process and Business Scenarios
24.2 SAP Forecasting and Replenishment
24.3 SAP Advance Planning and Optimization (SAP – APO)
24.4 SAP Inventory Collaboration Hub (SAP – OCH)
24.5 SAP Event Management (SAP – EM)
24.6 SCM Basis
25. SAP Netweaver
25.1 SAP Master data Management
25.2 Information Integration
25.3 Portal Content
25.4 Process Integration
25.5 Knowledge Management
25.6 Life Cycle Management
25.7 SAP Business Intelligence
25.8 SAP Visual Composer
25.9 People Integration
25.10 Application Platform
25.11 SAP Web Application Server
25.12 SAP Business Information Warehouse
25.13 SAP Solution Manager
25.14 SAP Enterprise Portal
25.15 SAP Mobile Engine
25.16 Security
26.
SAP IS (Industry Solutions) / SAP for Industries
SAP has the following industries specific solutions:
26.1 Aerospace & Defense
26.2 Consumer Products
26.3 Defense & Security
26.4 Retail
26.5 Insurance
26.6 Mill Products
26.7 Higher Education & Research
26.8 Industrial Machinery & Components
26.9 Logistics Service Providers
26.10 Automotive
26.11 Chemicals
26.12 Pharmaceuticals
26.13 Banking
26.14 Telecoms
26.15 Life Sciences
26.16 Mining
26.17 Public Sector
26.18 Service Provider
26.19 Media
26.20 Healthcare
26.21 Oil & Gas
26.22 Utilities
26.23 Postal Services











0 comments:
Post a Comment